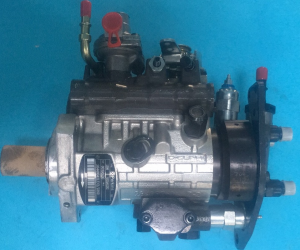
Diesel Fuel Injection Pump 150-2507 7C-4567 Engine Auto Engine Part
products description
| Reference Code | 150-2507 |
| MOQ | 1 PCS |
| Certification | ISO9001 |
| Place of Origin | China |
| Packaging | Neutral packing |
| Quality Control | 100% tested before shipment |
| Lead time | 7~15 working days |
| Payment | T/T, Western Union, Money Gram, Paypal, Alipay, Wechat |
Cavitation Mechanisms and Reliability Improvement of Engine Oil Pumps under High-Speed Operation
With the continuous increase in engine speed and power density, oil pumps are required to operate under more demanding conditions while maintaining stable lubrication performance. One critical challenge affecting oil pump reliability under high-speed operation is cavitation, which can lead to flow instability, noise, vibration, and long-term component damage. Understanding cavitation mechanisms and developing effective mitigation strategies are essential for improving oil pump durability and efficiency.
Cavitation in engine oil pumps typically occurs when local pressure at the pump inlet or within internal flow passages drops below the vapor pressure of the lubricating oil. High rotational speed, excessive suction resistance, and sudden changes in flow direction can all contribute to local pressure reduction. Once cavitation bubbles form, they collapse rapidly as pressure recovers, generating localized impact loads on pump surfaces. Repeated bubble collapse accelerates material erosion, particularly on gear teeth, rotor surfaces, and pump housing walls.
Experimental observations indicate that cavitation not only reduces volumetric efficiency but also disrupts oil flow continuity. During high-speed operation, cavitation-induced flow separation causes intermittent oil delivery, resulting in pressure fluctuations at the pump outlet. These pressure instabilities can adversely affect downstream lubrication systems, increasing wear on bearings and other critical engine components.
To improve cavitation resistance, inlet flow optimization is a primary design strategy. Enlarging inlet cross-sectional area, smoothing inlet transitions, and reducing sharp edges can significantly decrease pressure losses and improve oil filling capability. Additionally, optimizing internal flow channel geometry helps maintain uniform pressure distribution and prevents localized low-pressure zones.
Material selection and surface treatment also play an important role in enhancing cavitation resistance. Using high-strength alloys or applying surface coatings with improved hardness and erosion resistance can reduce cavitation-induced damage. Furthermore, refined surface finishing techniques minimize micro-defects that act as cavitation initiation sites.
From a system perspective, matching oil pump performance with engine operating conditions is essential. Variable-speed or electronically controlled oil pumps allow dynamic adjustment of pump speed according to lubrication demand, reducing unnecessary high-speed operation and lowering cavitation risk. Improved oil formulations with enhanced anti-foaming and cavitation resistance properties also contribute to more stable pump performance.
In conclusion, cavitation is a key factor limiting the reliability of engine oil pumps under high-speed conditions. Through optimized inlet design, improved internal flow paths, appropriate material selection, and intelligent control strategies, cavitation effects can be effectively mitigated. These measures not only enhance oil pump durability but also support stable lubrication and extended engine service life in modern high-performance engines.